
Creative Piece
Conservation of Energy

The digital video game created for this course is currently in place at the end of the fourth lesson however it can be used in many situations as the themes of conservation of energy between the bow and arrow fit this unit in many ways. There are also elements in the game that can be used to expand student learning or introduce further elements of the unit including topics surrounding Newton's Laws of Motion and making connections between the spring constant, potential energy, force, power and velocity.
How to Play
Use the arrow keys to move.
Use the mouse to shoot. The arrow will travel to where you click.
Prevent the enemies from reaching the castle. The game ends when the castle loses its health.
Defeat the bosses to gain valuable power-ups.
Choose your bow and arrow wisely. Your choice will vary the force of impact, the time to shoot and the velocity of the arrow.
Physics of the Bow
The amount of potential energy that can be stored in a bow is equal to the work done to stretch the bow string.
This depends on the spring constant (k) as well as the distance stretched (x).
Since Hooke’s Law says the force required to stretch the bow is directly proportional to the distance stretched, the potential energy stored in the bow depends on the spring constant (k).
The greater the value of k, the more energy in the bow.
The increased potential energy comes at a cost.
Assuming the archer generates consistent power, to achieve the greater levels of potential energy, more time will be required.
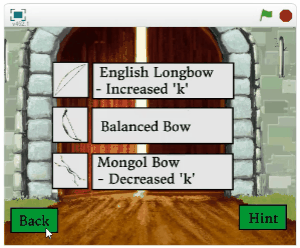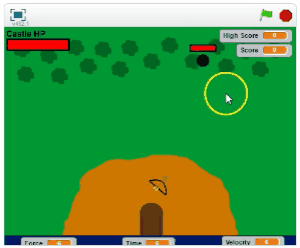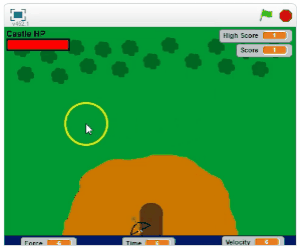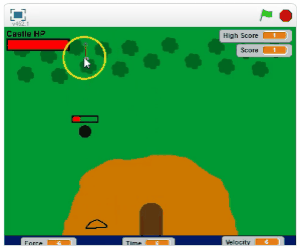
Choosing Your Bow
English Long Bow: increased k
Balanced bow: balanced k
Mongol bow: decreased k
Implications:
-
Heavy bow: more time but more PE (velocity and force)
-
Medium bow: balanced
-
Light bow: less time but less PE (velocity and force)
Physics of the Arrow
The amount of potential energy that can be stored in a bow is equal to the work done to stretch the bow string.
This depends on the spring constant (k) as well as the distance stretched (x).
Since Hooke’s Law says the force required to stretch the bow is directly proportional to the distance stretched, the potential energy stored in the bow depends on the spring constant (k).
The greater the value of k, the more energy in the bow.
The increased potential energy comes at a cost. Assuming the archer generates consistent power, to achieve the greater levels of potential energy, more time will be required.
Choosing Your Arrow
Broadhead Arrow: increased m
Balanced Arrow: balanced m
Bodkin Arrow: decreased m
Implications:
-
Broadhead Arrow: lower velocity, greater force (velocity and force)
-
Balanced arrow: balanced
-
Bodkin Arrow: greater velocity, lower force
